“The teaching of any arts subject […] is a cognitively sophisticated and demanding activity. It involves a subtle attention to detail, nuance and implication; the ability to exploit the unpredictable in the course of the work; the confidence to shift both educational and artistic goals where appropriate; and the security to deal with disappointment and possible failure.” (Dunn, 2016, p. 129)
As I venture into the last fews classes of my summer intensive course, Drama Education in Early Years, thoughts and ideas articulated during the composition of its two assignments, linger at the edges of my thinking. They move alongside questions, new thoughts, experiences, mingling and conversing with previous notions and those enkindled through my concurrent participation in Development and Implementation of the Curriculum in Art.
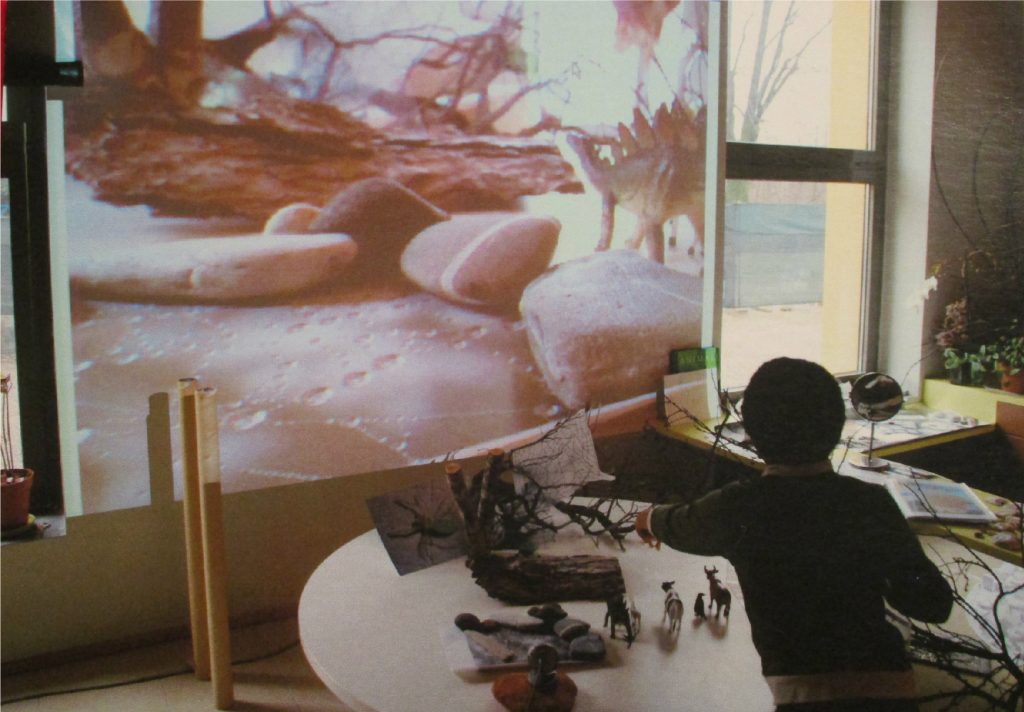
For the purpose of meeting the expectations and requirements of the above courses, I delved into an examination and overview of arts integrated activities meant to support children to think and learn with more-than-human-others (eg. trees, plants). As I had been previously acquainted, in both my research and practice as an early childhood educator, with notions of thinking “with materials” (Pacini-Ketchabaw et al., 2017, p. 1) and eradicating contradistinctions between human and natural worlds (“About the Collective”, 2020), it had been the content gained through Drama Education in Early Years that triggered questions, incited connections, and engendered new lines of thinking.
Questions, considerations:
The story-drama structures outlined in the course syllabus and required text, as well as the drama practices and exercises described in the course’s first required reading, incited the question: Can these structures and techniques be translated into my own teaching-learning environment? After encountering that first work from Lundy and Swartz (2011), whose drama techniques closely resembled those I had been acquainted with in high school, I wondered at the value of such within my free-flowing, malleable, inquiry-rich, emergent work with young children (see The Blog). However, further readings, class-work, and knowledge gained during research for the course’s first assignment, demonstrated the multifaceted, process focused, boundless nature of drama education. Soon, my concerns regarding the benefits of drama structures, were exchanged with considerations connected to how, when, with whom, where, and within what context could they be supported and implemented.
Making connections:
At the same time as I had been thinking and learning with Drama Education in Early Years, I had been thinking and learning with arts education and its required text. As I reacquainted myself with the material encounters of Pacini-Ketchabaw et al. (2017), I became acquainted with process drama through the work of Brown (2017) and Kana and Aitken (2007). At once, cross-curriculum experiences began to formulate, while connections in experiential, art, and drama theory and practice took hold. Progressing further into the course, more hypotheses, documentation, understandings framed those inclinations.
A material encounter (Pacini-Ketchabaw et al., 2017), as well as a process drama experience, generates space, setting, and opportunity for children to collectively, confront, construct, organize, challenge, and naturally expound predicaments and tensions, knowledge and experience, ideas and typical modes of understanding (p. 36; Brown, 2017, p. 165; Kana & Aitken, 2007, p. 700).
Brown (2017) has written:
“Role-playing through process drama activities promotes taking on multiple perspectives and provokes genuine open-mindedness; it facilitates construction of more fully elaborated and unique problem-solving models, and encourages cognitive and personal flexibility.” (p.169)
Within BC early learning (2019) contexts, educators are researchers and collaborators, rather than purveyors of knowledge. In process drama or a material encounter, the typical transfer of knowledge is altered, educators are supported to join in and become a part of the learning experience. Accordingly, children become active, rather than passive, participants in those moments of tension, problem solving, collaboration, understanding (McNaughton, 2004, p. 154)
Early childhood educator, Linda McDonell, in the below short video, briefly and fluidly articulates her transformation from expert to guide and the value of not knowing:
In a process drama experience, children are engaged and drawn in only when educators are prepared and willing to be spontaneous and take risks, to be equally immersed and affected by the experience, and to learn alongside them (Dunn, 2016, p. 129; Kana & Aikten, 2007, p. 700). Educators do not decide or hope for a particular outcome, but direct the focus of children’s experience by determining what materials to set out, which role to play, or seeking to answer a specific question. For this reason, neither a process drama, nor a material encounter, should be understood as a demonstration of what either should look like. As Dunn wrote: “Simply using the strategies of process drama does not constitute doing process drama!” (p. 134). Instead, the unknown, unexpected, unpredictable are exploited and embraced, and the aim is to engage children in encounters, moments, scenerios that might encourage them to develop an understanding and awareness of other perspectives, to support them to think critically, and generate space for them to further inquire, question, consider (Dunn, 2016, p. 129; Kana & Aitken, 2007, p. 700; Pacini-Ketchabaw et al., 2017).
New contexts for change:
The process of overviewing numerous arts and drama resources, aimed at supporting children to think and learn with plants and trees, apprised me of the potential for drama practices to promote social change and environmental awareness.
Pondering over drama activities and diving into research, I became immersed in a variety of imagined drama scenerios. I formulated structures that offered children opportunity to become plants or those creatures that live amongst them. I pictured myself generating “Formal Gatherings” (Booth, 2005) to save the plants with the children, . We’d ask ourselves: How can we help plants? What type of behaviours are respectful of plants? Together we’d facilitate a pretend protest to help save the plants. What would our signs say? What we would say? How would we say it? Who could the protesters be? What part would everyone else play? I reflected on these structures, wondered at these storylines: Would they more deeply engage children in learning and support them to think with the lives of more-than-human-others? Could they inspire change?
“The power of the drama is not simply that it teaches facts about the environment but that the narrative is a metaphor for environmental issues.” (McNaughton, 2004, p. 154)
In response to current environmental crises that include “climate change, species extinction, risks to […] food and water supplies, [etc.]” (BC Ministry of Education, 2019, p. 29), many pedagogical approaches have been reformed and reconsidered. The First People’s principles of learning and common worlds research collective have been introduced into BC’s updated Early Learning Framework (2019) in order to respond to both the Truth and Reconciliation Commission of Canada: Calls to Action (2015) and pressing environmental issues.
Some of the First People’s principles include:
- Teaching and learning that is relational, patient
- Focuses on connectedness and place, that supports family and community
- Involves recognizing the responsibility in one’s actions
(BC Ministry of Education, 2019, p. 14)
While, sustainability curriculums in Scottland include competencies such as:
- Sensitivity to and appreciation of the social and natural environment
- Knowledge/understanding of the social environment
- Skills to find out about and explore environmental issues
(McNaughton, 2004, p. 141)
Like McNaughton (2004), I began to carefully notice and consider the possibility that drama strategies might benefit teachers and learners by addressing many of the above principles and outcomes (p. 141).
In their work, Kana and Aitken (2007) explored the value of process drama in examining issues surrounding cultural exclusion and social injustice. They found that when exploring ideas related to injustice, such as the un-heard voices of specific Peoples or more-than-human-others, is it pertinent that both educator and student take on a range of positions, through role play, so that the complexity and diversity inherent in such issues might be recognized (p. 701). In addition, by providing oppportunity for learners to become immersed in dramatization they are able to develop a fresh perspective on the real-life situations resembled within (Kana & Aitken, 2007). While Brown (2017) also wrote, “the experience of believing and delving deeper into role can facilitate the development of empathy by provoking a deep awareness of other’s perspectives.” (p. 169)
Green (2017) also examined how role-play can support children to engage in empathetic reasoning, “to think about how it might feel to be someone or something else” (p. 14). By engaging children in role-play and encouraging dramatization, children are supported to carefully notice and pay attention to the characteristics of their environment and how they interact with it (Green, 2017, p. 6). Green felt that perspective taking and role-play orchestrated outdoors would generate further social engagements, stories, and dramatic play scenerios that incorporate elements of the natural world (p. 14).
These understandings, ideas, imagined scenes lingered, and continue to inch their way back into my reasoning as I move into different thoughts, am introduced to new ideas, and continue in my every-changing, emergent work with young children.
Until next time,
EJ
Coming up… My final reflective post connected to Drama Edcuation in Early Years. I will look more closely at how my learning might affect my current practice as an early childhood educator.
References
About the collective. (2020). http://commonworlds.net
Brown, V. (2017). Drama as a valuable learning medium in early childhood. Arts Education Policy Review, 118(3), 164-171. https://doi.org/10.1080/10632913.2016.1244780
Booth, D. (2005). Story drama (2nd ed.). Pembroke Publishers.
Dunn, J. (2016). Demystifying process drama: Exploring the why, what, and how. Nj: Drama Australia journal, 40(2), 127-140. doi:10.1080/14452294.2016.1276738
Green, C. (2017). Four methods for engaging young children as environmental education researchers. The International Journal of Early Childhood Environmental Education, 5(1), 6-19. https://naturalstart.org/sites/default/files/journal/ijecee_5_1_green.pdf
Kana, P., & Aitken, V. (2007). She didn’t ask me about my grandma: Using process drama to explore issues of cultural exclusion and educational leadership. Journal of Educational Administration, 45(6), 697-710. http://doi.org/10.1108/09578230710829883
Lundy, K., Swartz, L. (2011). Building community. In K. Revington (Ed.) Creating caring classrooms: How to encourage students to communicate, create, and be compassionate of others (pp.13 – 44). Pembroke.
McNaughton, M. J. (2004). Educational drama in the teaching of education for sustainability. Environmental Education Research, 10(2), 139-155. doi:10.1080/13504620242000198140
Ministry of Education (2019). British Columbia early learning framework. Victoria, B.C. Retrieved from https://www2.gov.bc.ca/gov/content/education-training/early-learning/teach/early-learning-framework
Pacini-Ketchabaw, V., Kind, S., & Kocher, Laurie L. M. (2017). Encounters with materials in early childhood education. Routledge.








Community